Rett Syndrome
Rett Syndrome
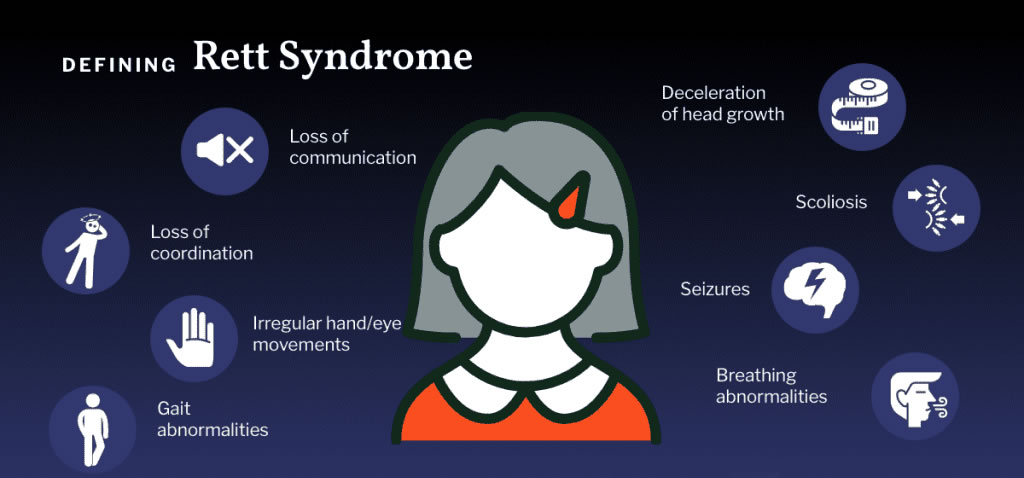
Rett Syndrome is a genetic disorder that affects girls almost exclusively. It is a rare form of autism that affects approximately one in every 10,000 to 15,000 girls. Girls with Rett Syndrome develop typically until about six months of age and then experience a regression in skills. They may lose their ability to speak, walk, and use their hands. They may also have seizures and breathing difficulties.
Rett Syndrome Overview
Rett Syndrome is a rare neurodevelopmental disorder that primarily affects girls. Rett Syndrome is a genetic disorder that affects brain development, resulting in severe cognitive and physical impairments. Rett Syndrome is primarily caused by mutations in the MECP2 gene, which is located on the X chromosome. The MECP2 gene provides instructions for producing a protein that plays a crucial role in brain development and function. Mutations in this gene disrupt the normal functioning of the protein, leading to the symptoms of Rett Syndrome. In approximately 95% of cases, Rett Syndrome is caused by a random mutation that occurs for the first time in the affected individual (de novo mutation). This means that the mutation is not inherited from the parents. In rare cases, Rett Syndrome can be inherited in families with a history of the disorder. Genetic testing can help confirm the presence of MECP2 mutations and aid in the diagnosis of Rett Syndrome.
Rett Syndrome Symptoms
Rett Syndrome is characterized by a range of symptoms that typically become noticeable between 6 and 18 months of age. It's important to note that the presentation and severity of symptoms can vary among individuals with Rett Syndrome.
- Loss of purposeful hand skills, such as grasping objects or gestures
- Developmental regression, where children lose previously acquired skills, such as crawling or walking
- Loss of verbal abilities or limited speech
- Repetitive hand movements, such as hand-wringing or hand-to-mouth movements
- Breathing irregularities, such as hyperventilation or breath-holding
- Motor difficulties, including problems with coordination and balance
- Social withdrawal and limited interest in interaction with others
Importance of Therapy for Rett Syndrome
Therapy plays a crucial role in the management and improvement of symptoms associated with Rett Syndrome. Since this condition affects multiple aspects of an individual's life, a comprehensive therapeutic approach can help maximize their potential and enhance their quality of life. Rett Syndrome therapy aims to address the core symptoms of the disorder, such as motor impairments, communication difficulties, and social interaction challenges. By targeting these areas, therapy can have a significant impact on the overall development and well-being of individuals with Rett Syndrome.
Physical therapy focuses on improving motor skills, mobility, and overall physical function in individuals with Rett syndrome. It employs a range of exercises and techniques tailored to the specific needs and abilities of the individual. The goals of physical therapy include enhancing muscle strength, improving balance and coordination, and maximizing functional independence. Physical therapy sessions often involve a variety of activities, including stretching exercises, range-of-motion exercises, and balance training. These exercises target specific muscle groups and help improve muscle tone, flexibility, and overall motor control. Additionally, physical therapists may utilize adaptive equipment and assistive devices to facilitate movement and enhance mobility.
Occupational therapy aims to enhance the individual's ability to perform daily activities, promote independence, and improve overall quality of life. Occupational therapists work closely with individuals with Rett syndrome to develop skills necessary for self-care, school, work, and leisure activities. They focus on improving fine motor skills, sensory integration, and cognitive abilities. During occupational therapy sessions, therapists may utilize various techniques and strategies to help individuals with Rett syndrome develop and refine skills such as dressing, feeding, grooming, and handwriting. They may also provide guidance on sensory integration techniques to help manage sensory sensitivities commonly observed in individuals with Rett syndrome.
Speech and language therapy is essential for individuals with Rett syndrome, as they often experience significant communication difficulties. Speech and language therapists work closely with individuals to address speech impairments, improve language skills, and enhance overall communication abilities. Therapists may employ a variety of techniques, including augmentative and alternative communication (AAC) systems, to facilitate communication in individuals with limited verbal abilities. AAC systems can include picture exchange communication systems (PECS), communication boards, or electronic devices with voice output. These tools enable individuals with Rett syndrome to express their needs, wants, and thoughts effectively.
Speech and language therapy also focuses on improving oral motor skills, such as swallowing and chewing, which may be impacted in individuals with Rett syndrome. Therapists provide exercises and strategies to enhance these abilities, ensuring better overall oral health and nutrition. By incorporating physical therapy, occupational therapy, and speech and language therapy, individuals with Rett syndrome can experience significant improvements in motor skills, communication abilities, and overall quality of life. It is important to tailor therapy approaches to the specific needs of each individual, ensuring that therapy sessions are engaging, effective, and supportive.
Behavior therapy, specifically Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA), is often utilized as an intervention for individuals with Rett syndrome. ABA focuses on understanding and modifying behaviors by implementing evidence-based techniques. It aims to teach individuals new skills, reduce challenging behaviors, and improve their overall functioning. Behavior therapy for individuals with Rett syndrome typically involves structured and individualized interventions. These interventions may include teaching adaptive skills, such as self-care, social interactions, and functional communication. Additionally, behavior therapy aims to reduce and manage challenging behaviors commonly associated with Rett syndrome, such as hand-wringing or self-injurious behaviors.
Understanding Rett Syndrome
Rett syndrome seems to be caused by mutations in the Methyl-CpG binding protein 2 (MECP2.) This protein is crucial for regulating the activity of genes involved in nervous system development and function. As a disorder marked by various comorbidities, RTT treatment requires a multidisciplinary approach:
- Neurologists may treat a patient’s seizures.
- Psychiatrists can offer psychological support.
- Sleep medicine specialists may sometimes manage mood and sleep disorders.
- Respiratory therapists, cardiologists, gastroenterologists, and orthopedists often round out the medical care team. There is no cure for Rett syndrome. But certain comorbidities typically associated with RTT are treatable. There are, for example, medications for epilepsy and anxiety-related GI and respiratory issues.